Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Hypothalamus and Pituitary Gland
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Descriptive Epidemiology and Survival Analysis of Prolactinomas and Cushing’s Disease in Korea
- Jin Sun Park, Soo Jin Yun, Jung Kuk Lee, So Young Park, Sang Ouk Chin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(3):688-696. Published online June 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1000
- 4,738 View
- 135 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Only a few studies have established the epidemiology of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease in Korea. Furthermore, the incidence of these disease are increasing than before associated with the development of technologies. This study was designed to evaluate the epidemiology of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease and their survival analysis according to treatment.
Methods
The nationwide, population-based study evaluated incidence and prevalence of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease using de-identified claims data in The Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service database between 2013 and 2017. The survival analysis investigated regarding treatment over a period of 6 years. A log-rank test and Cox proportional hazard regression analysis were used.
Results
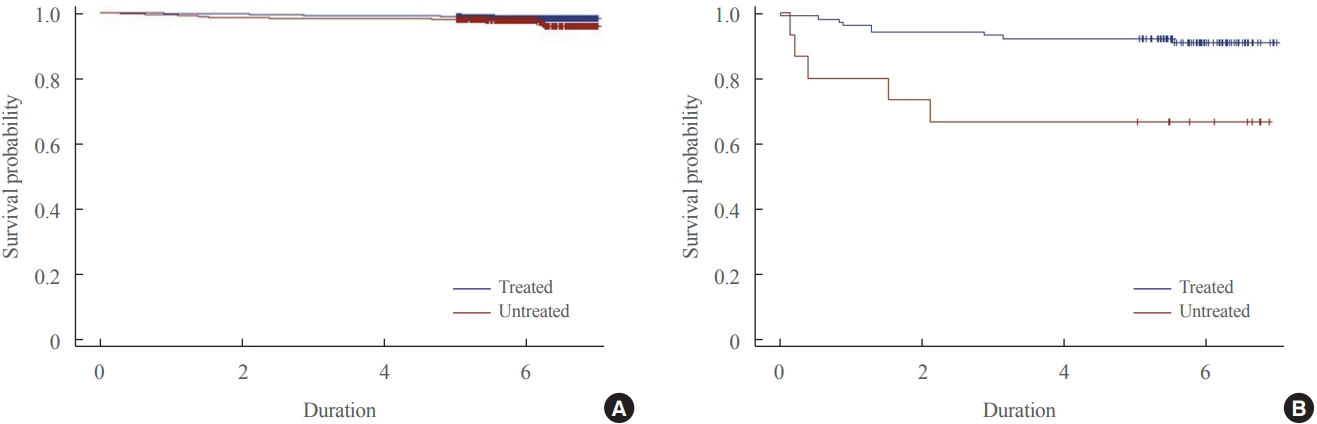
The 6,056 patients with newly diagnosed prolactinoma and 584 patients with Cushing’s disease were recorded between 2013 and 2017. The annual incidence of prolactinoma was 23.5 cases per million, and its prevalence was 82.5 cases per million, and 2.3 cases per million/year and 9.8 cases per million for Cushing’s disease. The survival benefit was insignificant in prolactinoma according to treatment, but treatment of Cushing’s disease ameliorated the survival rate significantly.
Conclusion
Overall, the incidence of prolactinoma and Cushing’s disease was similar with those found previously, but the prevalence of two diseases were inconsistent when compared with the early studies. The present study also proposed necessity of treatment in Cushing’s disease for improving the survival rate. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Cushing Syndrome
Martin Reincke, Maria Fleseriu
JAMA.2023; 330(2): 170. CrossRef - Clinical Biology of the Pituitary Adenoma
Shlomo Melmed, Ursula B Kaiser, M Beatriz Lopes, Jerome Bertherat, Luis V Syro, Gerald Raverot, Martin Reincke, Gudmundur Johannsson, Albert Beckers, Maria Fleseriu, Andrea Giustina, John A H Wass, Ken K Y Ho
Endocrine Reviews.2022; 43(6): 1003. CrossRef
- Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database

- Miscellaneous
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Growth Hormone Deficiency: A Position Statement from Korean Endocrine Society and Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology
- Jung Hee Kim, Hyun Wook Chae, Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyeong Hye Park, Dong Jun Lim, Kwang Joon Kim, Jung Soo Lim, Gyuri Kim, Yun Mi Choi, Seong Hee Ahn, Min Ji Jeon, Yul Hwangbo, Ju Hee Lee, Bu Kyung Kim, Yong Jun Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Hwa Young Ahn, Hoon Sung Choi, Sang Mo Hong, Dong Yeob Shin, Ji A Seo, Se Hwa Kim, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Hoon Yu, Byung Joon Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sung-Woon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Eun Jig Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):272-287. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.272
- 9,490 View
- 428 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
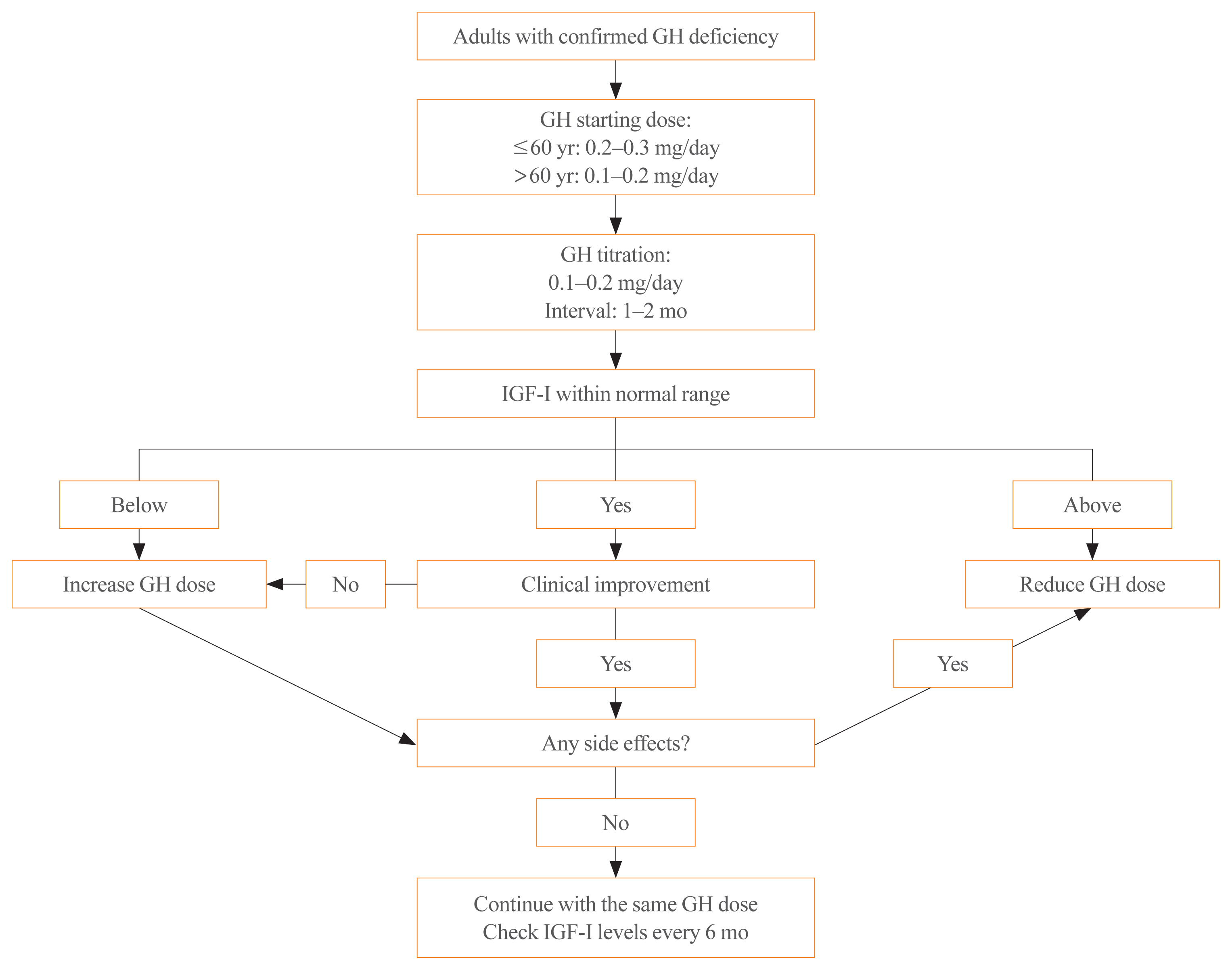
ePub - Growth hormone (GH) deficiency is caused by congenital or acquired causes and occurs in childhood or adulthood. GH replacement therapy brings benefits to body composition, exercise capacity, skeletal health, cardiovascular outcomes, and quality of life. Before initiating GH replacement, GH deficiency should be confirmed through proper stimulation tests, and in cases with proven genetic causes or structural lesions, repeated GH stimulation testing is not necessary. The dosing regimen of GH replacement therapy should be individualized, with the goal of minimizing side effects and maximizing clinical improvements. The Korean Endocrine Society and the Korean Society of Pediatric Endocrinology have developed a position statement on the diagnosis and treatment of GH deficiency. This position statement is based on a systematic review of evidence and expert opinions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial
Ghina Tsurayya, Cut Alifiya Nazhifah, Muhammad Rahmat Pirwanja, Putri Oktaviani Zulfa, Muhammad Raihan Ramadhan Tatroman, Fajar Fakri, Muhammad Iqhrammullah
Children.2024; 11(2): 227. CrossRef - Evaluation of Adult Height in Patients with Non-Permanent Idiopathic GH Deficiency
Agnese Murianni, Anna Lussu, Chiara Guzzetti, Anastasia Ibba, Letizia Casula, Mariacarolina Salerno, Marco Cappa, Sandro Loche
Endocrines.2023; 4(1): 169. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Possible Aid for Detecting Hypoglycemic Events during Insulin Tolerance Tests
Soo Yeun Sim, Moon Bae Ahn
Sensors.2023; 23(15): 6892. CrossRef - The risk patients with AGHD have of developing CVD
Eisha Javed, Maha Zehra, Naz Elahi
International Journal of Cardiology Cardiovascular Risk and Prevention.2023; 19: 200221. CrossRef - Diagnosis of GH Deficiency Without GH Stimulation Tests
Anastasia Ibba, Sandro Loche
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic Impacts of Discontinuation and Resumption of Recombinant Human Growth Hormone Treatment during the Transition Period in Patients with Childhood-Onset Growth Hormone Deficiency
Yun Jeong Lee, Yunha Choi, Han-Wook Yoo, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Han Saem Choi, Ho-Seong Kim, Jae Hyun Kim, Jung Eun Moon, Cheol Woo Ko, Moon Bae Ahn, Byung-Kyu Suh, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 359. CrossRef - A Radiomics-Based Model with the Potential to Differentiate Growth Hormone Deficiency and Idiopathic Short Stature on Sella MRI
Taeyoun Lee, Kyungchul Song, Beomseok Sohn, Jihwan Eom, Sung Soo Ahn, Ho-Seong Kim, Seung-Koo Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2022; 63(9): 856. CrossRef - Phenotypic spectrum of patients with mutations in CHD7: clinical implications of endocrinological findings
Ja Hye Kim, Yunha Choi, Soojin Hwang, Gu-Hwan Kim, Han-Wook Yoo, Jin-Ho Choi
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Endocrine Disorders: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Hyemi Kwon, Eun Roh, Chang Ho Ahn, Hee Kyung Kim, Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 839. CrossRef - Laron syndrome: clinic, diagnostics (а clinical case)
P.M. Lіashuk, R.P. Lіashuk, N.I. Stankova, M.B. Kudina
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(3): 193. CrossRef - Diagnosis for Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma: A Joint Position Statement of the Korean Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma Task Force
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Chang Ho Ahn, Kyung Ae Lee, Seung Hun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Kyeong Hye Park, Yun Mi Choi, Namki Hong, A Ram Hong, Sang-Wook Kang, Byung Kwan Park, Moon-Woo Seong, Myungshin Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(2): 322. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation Guidelines for Adrenal Tumor Ablation
Byung Kwan Park, Masashi Fujimori, Shu-Huei Shen, Uei Pua
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 553. CrossRef - Asian Conference on Tumor Ablation guidelines for renal cell carcinoma
Byung Kwan Park, Shu-Huei Shen, Masashi Fujimori, Yi Wang
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2021; 62(4): 378. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Treatment of Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency
Jung Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2021; 96(5): 400. CrossRef
- Once-Weekly Somapacitan as an Alternative Management of Growth Hormone Deficiency in Prepubertal Children: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trial

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Epidemiology of Functioning Pituitary Adenomas
- Sang Ouk Chin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):237-242. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.237
- 7,884 View
- 256 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
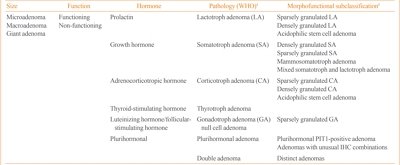
ePub - Pituitary adenomas (PAs) are defined as benign monoclonal tumors in the pituitary gland that cause symptoms due to either hormonal hypersecretion or a space-occupying effect, and are classified as functioning or non-functioning. Because of their rarity and slow-growing with symptomless nature in most cases, it has been challenging to investigate the epidemiology of PAs. Considering their public health impact and association with increased morbidity and mortality, however, it is essential to understand the prevalence and incidence of PAs in order to improve patient outcomes and to minimize the resultant burden on the health care system. Fortunately, developments in imaging modalities and easier access to large-scale population data have enabled investigators to analyze the epidemiology of PAs more accurately. This review summarizes previously reported epidemiologic data on functioning PAs in Korea and other countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spherical type of amyloidogenic pituitary prolactinoma in a 50 year old male
Madhala Divya, Balasubramanian Archana, Lawrence D Cruze, D. Balasubramanian
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery.2024; 36: 101957. CrossRef - Transcriptome of GH-producing pituitary neuroendocrine tumours and models are significantly affected by somatostatin analogues
Rihards Saksis, Olesja Rogoza, Helvijs Niedra, Kaspars Megnis, Ilona Mandrika, Inga Balcere, Liva Steina, Janis Stukens, Austra Breiksa, Jurijs Nazarovs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska, Ilze Konrade, Raitis Peculis, Vita Rovite
Cancer Cell International.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Models in Growth-Hormone- and Prolactin-Secreting Pituitary Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Systematic Review
Roxana-Ioana Dumitriu-Stan, Iulia-Florentina Burcea, Teodor Salmen, Catalina Poiana
Diagnostics.2023; 13(12): 2118. CrossRef - Salivary microbiome profiles for different clinical phenotypes of pituitary adenomas by single-molecular long-read sequencing
Xuefei Ji, Pingping Li, Qinglong Guo, Liao Guan, Peng Gao, Bingshan Wu, Hongwei Cheng, Jin Xiao, Lei Ye, Justin R. Kaspar
Microbiology Spectrum.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Endoscopic endonasal surgical management of giant pituitary adenomas with extension into ventricle system
Mykola O. Guk, Oleksii V. Ukrainets
Ukrainian Neurosurgical Journal.2023; 29(4): 13. CrossRef - Uso de resonancia magnética nuclear intraoperatoria en la resección transesfenoidal de adenomas hipofisiarios: ¿qué resultados se han obtenido?
María Laura Boschetti Saer, Levino Roberto Boschetti, Jose Pastor Linarez Veloz, Michael Ortega-Sierra
Archivos de Neurociencias.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of common and uncommon adult pituitary tumors in the U.S. according to the 2017 World Health Organization classification
Luz E. Castellanos, Catherine Gutierrez, Timothy Smith, Edward R. Laws, J. Bryan Iorgulescu
Pituitary.2022; 25(1): 201. CrossRef - The kinome, cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases of pituitary adenomas, a look into the gene expression profile among tumors from different lineages
Keiko Taniguchi-Ponciano, Lesly A. Portocarrero-Ortiz, Gerardo Guinto, Sergio Moreno-Jimenez, Erick Gomez-Apo, Laura Chavez-Macias, Eduardo Peña-Martínez, Gloria Silva-Román, Sandra Vela-Patiño, Jesús Ordoñez-García, Sergio Andonegui-Elguera, Aldo Ferreir
BMC Medical Genomics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - IL-10 Gene Rs1800871, Rs1800872, and Rs1800896 Polymorphisms and IL-10 Serum Levels Association with Pituitary Adenoma
Migle Palivonaite, Greta Gedvilaite, Brigita Glebauskiene, Loresa Kriauciuniene, Vita Rovite, Rasa Liutkeviciene
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 1921. CrossRef - Genome wide analysis of circulating miRNAs in growth hormone secreting pituitary neuroendocrine tumor patients’ plasma
Helvijs Niedra, Raitis Peculis, Helena Daiga Litvina, Kaspars Megnis, Ilona Mandrika, Inga Balcere, Mihails Romanovs, Liva Steina, Janis Stukens, Austra Breiksa, Jurijs Nazarovs, Jelizaveta Sokolovska, Rasa Liutkeviciene, Alvita Vilkevicute, Ilze Konrade,
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of mutant K-RAS in pituitary macroadenoma
Veronica Aran, Manoela Heringer, Paulo Jose da Mata, Leandro Kasuki, Renan Lyra Miranda, Felipe Andreiuolo, Leila Chimelli, Paulo Niemeyer Filho, Monica Roberto Gadelha, Vivaldo Moura Neto
Pituitary.2021; 24(5): 746. CrossRef - Surgery is a safe, effective first-line treatment modality for noninvasive prolactinomas
Ji Yong Park, Wonsuk Choi, A Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Woo-Youl Jang, Shin Jung, Ho-Cheol Kang
Pituitary.2021; 24(6): 955. CrossRef
- Spherical type of amyloidogenic pituitary prolactinoma in a 50 year old male

- Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland
- Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
- Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong Jun Lim, Dong Yeob Shin, Se Hwa Kim, Min Jeong Kwon, Ha Young Kim, Jin Hwa Kim, Dong Sun Kim, Chong Hwa Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(1):53-62. Published online March 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.1.53
- 6,459 View
- 253 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub The Korean Endocrine Society (KES) published clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of acromegaly in 2011. Since then, the number of acromegaly cases, publications on studies addressing medical treatment of acromegaly, and demands for improvements in insurance coverage have been dramatically increasing. In 2017, the KES Committee of Health Insurance decided to publish a position statement regarding the use of somatostatin analogues in acromegaly. Accordingly, consensus opinions for the position statement were collected after intensive review of the relevant literature and discussions among experts affiliated with the KES, and the Korean Neuroendocrine Study Group. This position statement includes the characteristics, indications, dose, interval (including extended dose interval in case of lanreotide autogel), switching and preoperative use of somatostatin analogues in medical treatment of acromegaly. The recommended approach is based on the expert opinions in case of insufficient clinical evidence, and where discrepancies among the expert opinions were found, the experts voted to determine the recommended approach.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors
Wooju Jeong, Sungrok Wang, Yumin Kim, Soohyun Lee, Minhu Huang, Jaeil Park, Myung-Han Yoon, Chang-Myung Oh, Cheol Ryong Ku
Smart Materials in Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: A Position Statement of the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Ho-Cheol Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 175. CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Revisiting the usefulness of the short acute octreotide test to predict treatment outcomes in acromegaly
Montserrat Marques-Pamies, Joan Gil, Elena Valassi, Marta Hernández, Betina Biagetti, Olga Giménez-Palop, Silvia Martínez, Cristina Carrato, Laura Pons, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Marta Araujo-Castro, Concepción Blanco, Inmaculada Simón, Andreu Simó-Servat, Gemm
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Bone Health in Patients with Thyroid Diseases: a Position Statement from the Korean Thyroid Association
A Ram Hong, Hwa Young Ahn, Bu Kyung Kim, Seong Hee Ahn, So Young Park, Min-Hee Kim, Jeongmin Lee, Sun Wook Cho, Ho-Cheol Kang
International Journal of Thyroidology.2022; 15(1): 1. CrossRef - Octreotide in the treatment of acromegaly – the possibilities of high-dose therapy
I. A. Ilovayskaya
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (10): 148. CrossRef - Approach of Acromegaly during Pregnancy
Alexandru Dan Popescu, Mara Carsote, Ana Valea, Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Ionela Teodora Dascălu, Tiberiu Tircă, Jaqueline Abdul-Razzak, Mihaela Jana Țuculină
Diagnostics.2022; 12(11): 2669. CrossRef - Left to themselves: Time to target chronic pain in childhood rare diseases
Christine B. Sieberg, Alyssa Lebel, Erin Silliman, Scott Holmes, David Borsook, Igor Elman
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2021; 126: 276. CrossRef - Severe respiratory failure in a patient with COVID-19 and acromegaly: rapid improvement after adding octreotide
Jacob Luty, LesleAnn Hayward, Melanie Jackson, P Barton Duell
BMJ Case Reports.2021; 14(8): e243900. CrossRef - Precision Therapy in Acromegaly Caused by Pituitary Tumors: How Close Is It to Reality?
Cheol Ryong Ku, Vladimir Melnikov, Zhaoyun Zhang, Eun Jig Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 206. CrossRef - Medical Treatment with Somatostatin Analogues in Acromegaly: Position Statement
Sang Ouk Chin, Cheol Ryong Ku, Byung Joon Kim, Sung-Woon Kim, Kyeong Hye Park, Kee Ho Song, Seungjoon Oh, Hyun Koo Yoon, Eun Jig Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Soo Lim, Jung Hee Kim, Kwang Joon Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Dae Jung Kim, Kyung Ae Lee, Seong-Su Moon, Dong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2019; 94(6): 485. CrossRef
- Hydrogel-fiber-mesh-based 3D cell cultures: A new method for studying pituitary tumors

- Clinical Study
- Correlation of Glypican-4 Level with Basal Active Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Level in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sang Ah Lee, Gwanpyo Koh, Suk Ju Cho, So-Yeon Yoo, Sang Ouk Chin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2016;31(3):439-445. Published online September 26, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2016.31.3.439
- 4,045 View
- 41 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Previous studies have reported that glypican-4 (GPC4) regulates insulin signaling by interacting with insulin receptor and through adipocyte differentiation. However, GPC4 has not been studied with regard to its effects on clinical factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to identify factors associated with GPC4 level in T2DM.
Methods Between January 2010 and December 2013, we selected 152 subjects with T2DM and collected serum and plasma into tubes pretreated with aprotinin and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor to preserve active gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). GPC4, active GLP-1, active GIP, and other factors were measured in these plasma samples. We performed a linear regression analysis to identify factors associated with GPC4 level.
Results The subjects had a mean age of 58.1 years, were mildly obese (mean body mass index [BMI], 26.1 kg/m2), had T2DM of long-duration (mean, 101.3 months), glycated hemoglobin 7.5%, low insulin secretion, and low insulin resistance (mean homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR], 1.2). Their mean GPC4 was 2.0±0.2 ng/mL. In multivariate analysis, GPC4 was independently associated with age (β=0.224,
P =0.009), and levels of active GLP-1 (β=0.171,P =0.049) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST; β=–0.176,P =0.043) after being adjusted for other clinical factors.Conclusion GPC4 was independently associated with age, active GLP-1, and AST in T2DM patients, but was not associated with HOMA-IR and BMI, which are well known factors related to GPC4. Further study is needed to identify the mechanisms of the association between GPC4 and basal active GLP-1 levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How Reliable are Commercially Available Glypican4 ELISA
Kits?
Joseph P. Buhl, Antje Garten, Jürgen Kratzsch, Wieland Kiess, Melanie Penke
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2022; 130(02): 110. CrossRef - Serum glypican-4 is associated with the 10-year clinical outcome of patients with peripheral artery disease
Axel Muendlein, Christine Heinzle, Andreas Leiherer, Kathrin Geiger, Eva Maria Brandtner, Stella Gaenger, Peter Fraunberger, Christoph H. Saely, Heinz Drexel
International Journal of Cardiology.2022; 369: 54. CrossRef - Berberine activates the β-catenin/TCF4 signaling pathway by down-regulating miR-106b to promote GLP-1 production by intestinal L cells
Jiao Wang, Li-Rui Wei, Yan-Ling Liu, Cheng-Zhi Ding, Feng Guo, Jiao Wang, Qian Qin, Feng-Jiao Huang, Ying Xin, Sheng-Nan Ma, Qiu-Ran Zhai, Shou-Jun Wang, Gui-Jun Qin
European Journal of Pharmacology.2021; 911: 174482. CrossRef - Increased Glypican-4 Levels Are Associated with Obesity in Adolescents
Huseyin Dag, Nevin Cetin Dag, Okan Dikker
Iranian Journal of Pediatrics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum glypican 4 level in obese children and its relation to degree of obesity
Chutima Leelalertlauw, Manassawee Korwutthikulrangsri, Pat Mahachoklertwattana, Suwannee Chanprasertyothin, Patcharin Khlairit, Sarunyu Pongratanakul, Preamrudee Poomthavorn
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(6): 689. CrossRef - Articles inEndocrinology and Metabolismin 2016
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 62. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Single‐ or Double‐Drug Antidiabetic Regimens in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Meta‐Analysis
Xi‐Ling Yang, Mi‐Ma Duo‐Ji, Zi‐Wen Long
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2017; 118(12): 4536. CrossRef
- How Reliable are Commercially Available Glypican4 ELISA
Kits?

- Obesity and Metabolism
- Apolipoprotein B Is Related to Metabolic Syndrome Independently of Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Younghyup Lim, Soyeon Yoo, Sang Ah Lee, Sang Ouk Chin, Dahee Heo, Jae Cheol Moon, Shinhang Moon, Kiyoung Boo, Seong Taeg Kim, Hye Mi Seo, Hyeyoung Jwa, Gwanpyo Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(2):208-215. Published online June 30, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.2.208
- 4,549 View
- 46 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Increased low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level and the presence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) are important risk factors for cardiovascular disease (CVD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Recent studies demonstrated apolipoprotein B (apoB), a protein mainly located in LDL-C, was an independent predictor of the development of CVD especially in patients with T2DM. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between apoB and MetS in T2DM patients.
Methods We analyzed 912 patients with T2DM. Fasting blood samples were taken for glycated hemoglobin, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, total cholesterol, triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C, and apoB. MetS was defined by the modified National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. We performed a hierarchical regression analysis with apoB as the dependent variable. Age, sex, the number of components of MetS and LDL-C were entered at model 1, the use of lipid-lowering medications at model 2, and the individual components of MetS were added at model 3.
Results Seventy percent of total subjects had MetS. ApoB level was higher in subjects with than those without MetS (104.5±53.3 mg/dL vs. 87.7±33.7 mg/dL,
P <0.01) even after adjusting for LDL-C. ApoB and LDL-C were positively correlated to the number of MetS components. The hierarchical regression analysis showed that the increasing number of MetS components was associated with higher level of apoB at step 1 and step 2 (β=0.120,P <0.001 and β=0.110,P <0.001, respectively). At step 3, TG (β=0.116,P <0.001) and systolic blood pressure (β=0.099,P <0.05) were found to significantly contribute to apoB.Conclusion In patients with T2DM, apoB is significantly related to MetS independently of LDL-C level. Of the components of MetS, TG, and systolic blood pressure appeared to be determinants of apoB.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- ApoB100 and Atherosclerosis: What’s New in the 21st Century?
Dimitris Kounatidis, Natalia G. Vallianou, Aikaterini Poulaki, Angelos Evangelopoulos, Fotis Panagopoulos, Theodora Stratigou, Eleni Geladari, Irene Karampela, Maria Dalamaga
Metabolites.2024; 14(2): 123. CrossRef - Association of apolipoproteins and lipoprotein(a) with metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Juan R. Ulloque-Badaracco, Ali Al-kassab-Córdova, Enrique A. Hernandez-Bustamante, Esteban A. Alarcon-Braga, Miguel Huayta-Cortez, Ximena L. Carballo-Tello, Rosa A. Seminario-Amez, Percy Herrera-Añazco, Vicente A. Benites-Zapata
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Current Data and New Insights into the Genetic Factors of Atherogenic Dyslipidemia Associated with Metabolic Syndrome
Lăcramioara Ionela Butnariu, Eusebiu Vlad Gorduza, Elena Țarcă, Monica-Cristina Pânzaru, Setalia Popa, Simona Stoleriu, Vasile Valeriu Lupu, Ancuta Lupu, Elena Cojocaru, Laura Mihaela Trandafir, Ștefana Maria Moisă, Andreea Florea, Laura Stătescu, Minerva
Diagnostics.2023; 13(14): 2348. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein B compared with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in the atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases risk assessment
Federica Galimberti, Manuela Casula, Elena Olmastroni
Pharmacological Research.2023; 195: 106873. CrossRef - Circulating lipids and breast cancer prognosis in the Malmö diet and cancer study
Sixten Harborg, Thomas P. Ahern, Maria Feldt, Ann H. Rosendahl, Deirdre Cronin-Fenton, Olle Melander, Signe Borgquist
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment.2022; 191(3): 611. CrossRef - Metabolic disorders in patients with impaired glucose tolerance, with or without underlying ischaemic heart disease
Milena Brkić, Danijel Đekić, Jelena Jovanić, Goran Topić, Aleksandra Grbić, Tatjana Šutilović
Scripta Medica.2022; 53(3): 175. CrossRef - Genetics of Cholesterol-Related Genes in Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of Current Evidence
Sok Kuan Wong, Fitri Fareez Ramli, Adli Ali, Nurul ‘Izzah Ibrahim
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3239. CrossRef - Prevalence of ApoB100 rs693 gene polymorphism in metabolic syndrome among female students at King Abdulaziz University
Rana A. Alghamdi, Maryam H. Al-Zahrani, Maha J. Balgoon, Nuha A. Alkhattabi
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2021; 28(6): 3249. CrossRef - Local ablation of gastric cancer by reconstituted apolipoprotein B lipoparticles carrying epigenetic drugs
Chia-Lung Yang, Ying-Jui Chao, Hao-Chen Wang, Ya-Chin Hou, Caleb Gonshen Chen, Chia-Ching Chang, Yan-Shen Shan
Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine.2021; 37: 102450. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Biomarkers of Obesity and Overlap With Cardiometabolic Dysfunction
Emily S. Lau, Samantha M. Paniagua, Shahrooz Zarbafian, Udo Hoffman, Michelle T. Long, Shih‐Jen Hwang, Paul Courchesne, Chen Yao, Jiantao Ma, Martin G. Larson, Daniel Levy, Ravi V. Shah, Jennifer E. Ho
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The association of ecg TV1>TV6 phenomenon as electrophysiological sign of metabolic myocardial disorders with risk factors for ischemic heart disease in the population of 25–44 years
N. A. Kuzminykh, L. V. Shcherbakova, V. S. Shramko, D. V. Denisova, Yu. I. Ragino
Ateroscleroz.2021; 17(2): 22. CrossRef - Regulation of Apolipoprotein B by Natural Products and Nutraceuticals: A Comprehensive Review
Mohammad Bagherniya, Thomas P. Johnston, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(7): 1363. CrossRef - Apolipoprotein B and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol reveal a high atherogenicity in individuals with type 2 diabetes and controlled low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
Liliana Fonseca, Sílvia Paredes, Helena Ramos, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Palma
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Menopause-Associated Lipid Metabolic Disorders and Foods Beneficial for Postmenopausal Women
Seong-Hee Ko, Hyun-Sook Kim
Nutrients.2020; 12(1): 202. CrossRef - Lipoprotein A, combined with alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase, contributes to predicting the occurrence of NASH: a cross-sectional study
Yu Zhang, He He, Yu-Ping Zeng, Li-Dan Yang, Dan Jia, Zhen-Mei An, Wei-Guo Jia
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel and traditional lipid profiles in Metabolic Syndrome reveal a high atherogenicity
Sílvia Paredes, Liliana Fonseca, Laura Ribeiro, Helena Ramos, José Carlos Oliveira, Isabel Palma
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum apolipoprotein B is associated with increased risk of metabolic syndrome among middle‐aged and elderly Chinese: A cross‐sectional and prospective cohort study
Rui Du, Xueyan Wu, Kui Peng, Lin Lin, Mian Li, Yu Xu, Min Xu, Yuhong Chen, Donghui Li, Jieli Lu, Yufang Bi, Weiqing Wang, Guang Ning
Journal of Diabetes.2019; 11(9): 752. CrossRef - The role of metabolism disorders, inflammation, myocardial injury in development chronic heart failure in metabolic syndrome patients
A. P. Roytman, T. A. Fedorova, E. A. Ivanova, A. V. Bugrov, V. V. Dolgov
Laboratornaya sluzhba.2018; 7(4): 5. CrossRef - Serum apoB levels independently predict the development of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A 7‐year prospective study
Jinghua Wang, Wanlin Zhu, Shujun Huang, Lei Xu, Min Miao, Chenjiao Wu, Chaohui Yu, Youming Li, Chengfu Xu
Liver International.2017; 37(8): 1202. CrossRef - Comprehensive assessment of lipoprotein subfraction profiles according to glucose metabolism status, and association with insulin resistance in subjects with early-stage impaired glucose metabolism
Jie-Eun Lee, Se Hee Min, Dong-Hwa Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim
International Journal of Cardiology.2016; 225: 327. CrossRef - Association of Serum Apolipoprotein B with the Increased Risk of Diabetes in Korean Men
Hyo Hee Lim, Oh Yoen Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2016; 5(3): 204. CrossRef
- ApoB100 and Atherosclerosis: What’s New in the 21st Century?

- Thyroid
- Celiac Disease in a Predisposed Subject (HLA-DQ2.5) with Coexisting Graves' Disease
- In Kyoung Hwang, Seon Hye Kim, Unjoo Lee, Sang Ouk Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sung-Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim, Suk Chon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(1):105-109. Published online March 27, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.1.105
- 3,738 View
- 32 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Celiac disease is an intestinal autoimmune disorder, triggered by ingestion of a gluten-containing diet in genetically susceptible individuals. The genetic predisposition is related to human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class II genes, especially HLA-DQ2-positive patients. The prevalence of celiac disease has been estimated to be ~1% in Europe and the USA, but it is rarer and/or underdiagnosed in Asia. We report a case of celiac disease in a predisposed patient, with a HLA-DQ2 heterodimer, and Graves' disease that was treated successfully with a gluten-free diet. A 47-year-old woman complained of persistent chronic diarrhea and weight loss over a 9 month period. Results of all serological tests and stool exams were negative. However, the patient was found to carry the HLA DQ2 heterodimer. Symptoms improved after a gluten-free diet was initiated. The patient has been followed and has suffered no recurrence of symptoms while on the gluten-free diet. An overall diagnosis of celiac disease was made in a genetically predisposed patient (HLA-DQ2 heterodimer) with Graves' disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Celiac Disease Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Standard Therapy for Japanese Patients
Tasuku Tamai, Kenji Ihara
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2075. CrossRef - Underutilization of diagnostic assays for celiac disease in Korea
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Olmesartan is not associated with the risk of enteropathy: a Korean nationwide observational
cohort study
Seng Chan You, Hojun Park, Dukyong Yoon, Sooyoung Park, Boyoung Joung, Rae Woong Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(1): 90. CrossRef - Prevalence of celiac disease in Asia: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Prashant Singh, Shubhangi Arora, Alka Singh, Tor A Strand, Govind K Makharia
Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2016; 31(6): 1095. CrossRef
- Celiac Disease Genetics, Pathogenesis, and Standard Therapy for Japanese Patients

- Adrenal gland
- Acromegaly due to a Macroinvasive Plurihormonal Pituitary Adenoma and a Rectal Carcinoid Tumor
- Sang Ouk Chin, Jin-Kyung Hwang, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Misu Lee, Natalia S. Pellegata, Sung-Woon Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):389-394. Published online January 5, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2015.30.3.389
- 3,708 View
- 41 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A macroinvasive pituitary adenoma with plurihormonality usually causes acromegaly and hyperprolactinemia, and also accompanies with neurologic symptoms such as visual disturbances. However, its concurrent presentation with a rectal carcinoid tumor is rarely observed. This study reports the history, biochemical, colonoscopic and immunohistochemical results of a 48-year-old female with acromegaly and hyperprolactinemia. Despite the large size and invasive nature of the pituitary adenoma to adjacent anatomical structures, she did not complain of any neurologic symptoms such as visual disturbance or headache. Immunohistochemical staining of the surgical specimen from the pituitary adenoma revealed that the tumor cells were positive for growth hormone (GH), prolactin (PRL), and thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). Staining for pituitary-specific transcription factor-1 (Pit-1) was shown to be strongly positive, which could have been possibly contributing to the plurihormonality of this adenoma. Colonoscopy found a rectal polyp that was identified to be a carcinoid tumor using immunohistochemical staining. A macroinvasive pituitary adenoma with concomitant rectal carcinoid tumor was secreting GH, PRL, and TSH, which were believed to be in association with over-expression of Pit-1. This is the first case report of double primary tumors comprising a plurihormonal pituitary macroadenoma and rectal carcinoid tumor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Cosecreting Thyroid Stimulating Hormone or Prolactin Pituitary Growth Hormone Adenomas: A Case-Control Study
Caiyan Mo, Han Chen, Jian Xu, Ying Guo, Yao Wang, Zheng Li, Tao Tong, Songbai Gui, Liyong Zhong
Endocrine Practice.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Growth Hormone Excess: Implications and Management
Suneela Dhaneshwar, Shrishti Shandily, Vatsalya Tiwari
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(6): 748. CrossRef - Pleiomorphism plurihormonal Pit-1-positive macroadenoma with central hyperthyroidism: a rare case report and literature review
Guiliang Peng, Chuanhong Guo, Yangfan Lv, Dandan Li, Ling Zhou, Rufei Shen, Yong Chen, Xin Zheng, Zheng Sun, Hongting Zheng, Min Long
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics and Management of Cosecreting Thyroid Stimulating Hormone or Prolactin Pituitary Growth Hormone Adenomas: A Case-Control Study

- Thyroid
- Insufficient Experience in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Leads to Misdiagnosis of Thyroid Cancer
- Jung Il Son, Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-taek Woo, Won Seo Park, Jong Kyu Byun, Yu-Jin Kim, Ja Min Byun, Sang Ouk Chin, Suk Chon, Seungjoon Oh, Sung Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2014;29(3):293-299. Published online September 25, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2014.29.3.293
- 4,134 View
- 34 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) of the thyroid is a widely accepted confirmatory test for thyroid cancer with high sensitivity and specificity. FNA is a simple procedure that is learned by many clinicians to enable accurate diagnosis of thyroid cancer. However, it is assumed that because the FNA test is a relatively simple procedure, its cytologic results are reliable regardless of the operator's experience. The aim of this study was to evaluate the differences in the diagnostic indices of FNA between operators with different levels of experience.
Methods A total of 694 thyroid FNA specimens from 469 patients were reviewed, and were separated based on the experience of the clinicians who performed the procedure. One hundred and ninety were categorized in the experienced group, and 504 in the inexperienced group. All FNA results were then compared with histological data from surgically resected specimens, and the sample adequacy and diagnostic accuracy of the groups were compared.
Results The age, gender, and nodule size and characteristics were similar in both groups. The sample adequacy rate was not significantly different between the experienced and nonexperienced groups (96.3% vs. 95.4%,
P =0.682). However, the non-experienced group had a higher false-negative rate than the experienced group (6.4% vs. 17.2%,P =0.038), and the sensitivity of the FNA test also tended to be lower in the nonexperienced group (95.6% vs. 88.9%,P =0.065).Conclusion These results suggest that FNA operators who have less experience may miss cases of thyroid cancer by performing the procedure incorrectly. As such, the experience of the FNA operator should be considered when diagnosing thyroid cancer. When clinicians are being trained in FNA, more effort should be made to increase the accuracy of the procedure; therefore, enhanced teaching programs and/or a more detailed feedback system are recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Role of MMP-9 and MMP-9 Inhibition in Different Types of Thyroid Carcinoma
Zhenshengnan Li, Jia Wei, Bowen Chen, Yaoqi Wang, Shuai Yang, Kehui Wu, Xianying Meng
Molecules.2023; 28(9): 3705. CrossRef - Telecytology rapid onsite evaluation, with real-time communication between cytopathologist, cytotechnologist, and proceduralist, offers better adequacy rates for lymph node, but not thyroid, fine-needle aspirations
Robert Post, Kelly Doxzon, Allison Goldberg
Journal of the American Society of Cytopathology.2023; 12(6): 407. CrossRef - Needle Biopsy Adequacy in the Era of Precision Medicine and Value-Based Health Care
Kenneth P. H. Pritzker, Heikki J. Nieminen
Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine.2019; 143(11): 1399. CrossRef - The expression profile of integrin receptors and osteopontin in thyroid malignancies varies depending on the tumor progression rate and presence of BRAF V600E mutation
Galina Chernaya, Nina Mikhno, Tatiana Khabalova, Svetlana Svyatchenko, Lyudmila Mostovich, Sergey Shevchenko, Lyudmila Gulyaeva
Surgical Oncology.2018; 27(4): 702. CrossRef - Can thyroid surgery be decided based on ultrasonographic findings, irrespective of cytopathological findings? Five-year retrospective study in a district general hospital
A.A. Elsayed, C. Murdoch, S. Murray, K. Bashir
Clinical Radiology.2017; 72(2): 170. CrossRef - Efficacy of ultrasound‐guided fine‐needle aspiration performed by surgeons newly trained in thyroid ultrasound
Agnaldo J. Graciano, Carlos A. Fischer, Carlos T. Chone, Giuliano S. Bublitz, Marina Sonagli, Cezar A. Rodrigues Filho
Head & Neck.2017; 39(3): 439. CrossRef - Usefulness of NRAS codon 61 mutation analysis and core needle biopsy for the diagnosis of thyroid nodules previously diagnosed as atypia of undetermined significance
Eun Kyung Jang, Won Gu Kim, Eui Young Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Yun Mi Choi, Min Ji Jeon, Jung Hwan Baek, Jeong Hyun Lee, Tae Yong Kim, Young Kee Shong, Jene Choi, Dong Eun Song, Won Bae Kim
Endocrine.2016; 52(2): 305. CrossRef - Articles in 'Endocrinology and Metabolism' in 2014
Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Carcinosarcoma of the Thyroid Gland
Mehmet Fatih Ekici, Cengiz Kocak, Zülfü Bayhan, Sezgin Zeren, Faik Yaylak, Mehmet Hüseyin Metineren, Fatma Emel Kocak
Case Reports in Surgery.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Letter: Insufficient Experience in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Leads to Misdiagnosis of Thyroid Cancer (Endocrinol Metab2014;29:293-9, Jung Il Son et al.)
Hyon-Seung Yi, Sihoon Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(4): 590. CrossRef - Response: Insufficient Experience in Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Leads to Misdiagnosis of Thyroid Cancer (Endocrinol Metab2014;29:293-9, Jung Il Son et al.)
Jung Il Son, Jeong-taek Woo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2014; 29(4): 592. CrossRef
- The Role of MMP-9 and MMP-9 Inhibition in Different Types of Thyroid Carcinoma


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



